It has long been assumed that lifespan and health are strongly correlated, but although there has been an overall increase in human life expectancy in recent decades, it is too often accompanied by deterioration of health.
A new study published on February 26 in Nature shows the influence of two epigenetic regulators on aging. Scientists led by Jie Yuan from the Chinese Academy of Sciences in Shanghai have studied the BAZ-2 and SET-6 proteins in Caenorhabditis elegans worms, which are orthologs of the human proteins BAZ2B and EHMT1.
Through genome-wide RNA-interference-based screening of genes that regulate behavioral deterioration in aging C. elegans, the researchers identified 59 genes as potential health modulators during aging. Essentially the proteins expressed by these genes, read and write epigenetic signals.
Among these modulators, they found that a neuronal epigenetic reader, BAZ-2, and a neuronal histone SET-6, accelerate the deterioration of the behavior of C. elegans by reducing the mitochondrial function, and repressing the expression of the encoded mitochondrial proteins. in the cell nucleus.
The researchers found that the levels of the two proteins increase with age in C. elegans and mice, which in turn attenuates the expression of genes involved in mitochondrial function.
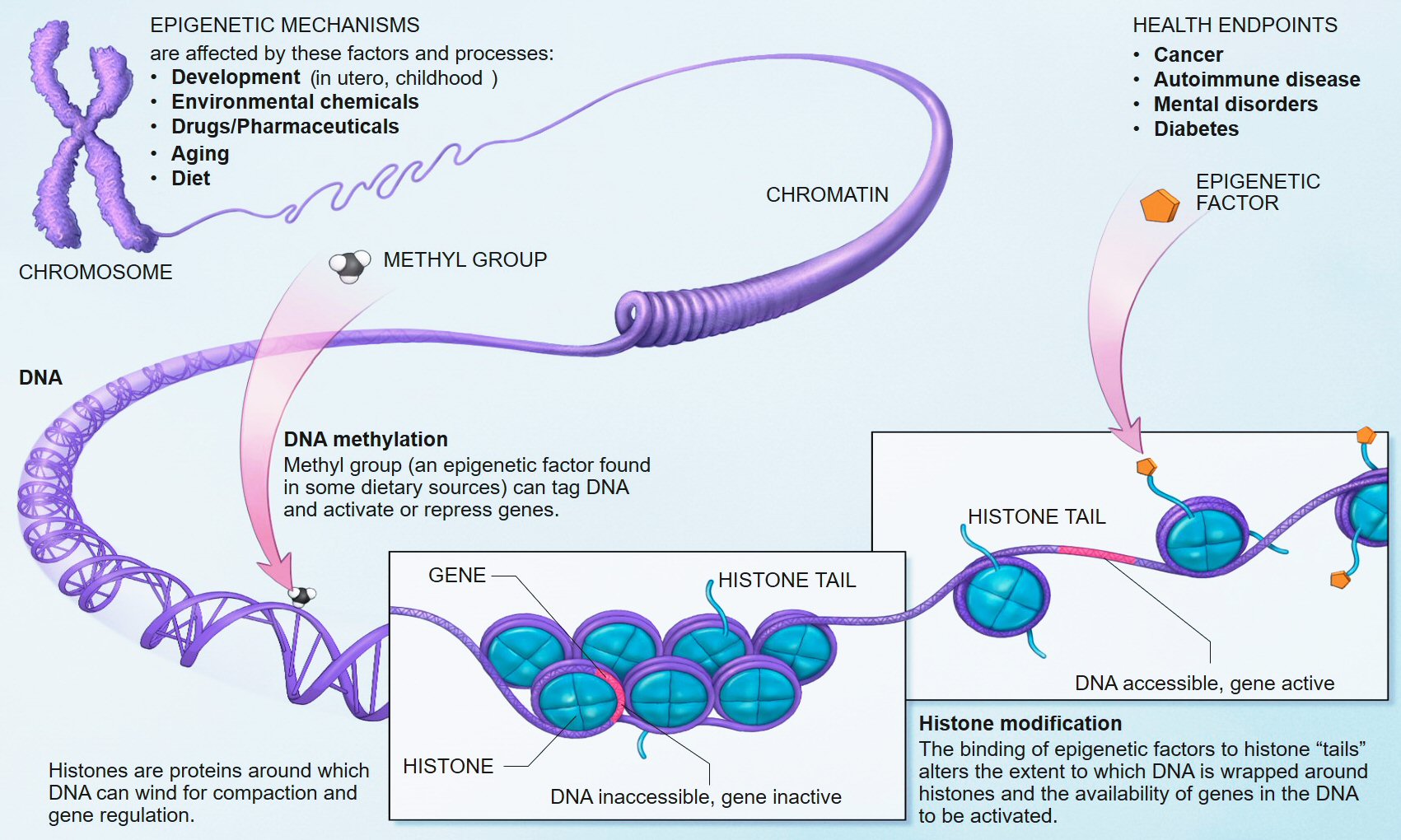
BAZ-2 and SET-6 are complementary epigenetic mechanisms. SET-6 is an "epigenetic writer" and BAZ-2 is an "epigenetic reader" which recognizes modified histones and recruits transcriptional regulators.
Histones are proteins located in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. They are the main protein components of chromosomes. They are closely associated with DNA and allow their compaction, but they also modify the expression of proteins by various epigenetic mechanisms known as the "histone code".
 Source Wikipedia.
Source Wikipedia.
How do BAZ-2 and SET-6 accelerate aging? The researchers found that the two proteins bind together to the promoter regions of more than 2,000 genes, and decrease their expression via methylation of histones. Among these target genes are many mitochondrial genes encoded nuclear. By suppressing the expression of these genes, BAZ-2 and SET-6 reduce oxygen consumption and ATP production, and decrease the critical stress responses that maintain mitochondrial proteostasis. The resulting metabolic slowdown discourages the worms from assimilating their food and they mate less.
This mechanism is conserved in the neurons of cultured mice and human cells. What about the orthologs of these epigenetic proteins in humans? A review of the databases shows that expression by human orthologs of the two proteins mentioned above, BAZ2B and EHMT1, increases with age and is positively correlated with the progression of Alzheimer's disease. Researchers have verified that ablation of BAZ-2 mouse ortholog Baz2b attenuates age-dependent body weight gain and prevents cognitive decline in aging mice.
 While wild-type mice grew fat with age, animals lacking both copies of the epigenetic reader Baz2b stayed trim, indicating improved mitochondrial function. [Yuan et al., Nature, 2020.]
While wild-type mice grew fat with age, animals lacking both copies of the epigenetic reader Baz2b stayed trim, indicating improved mitochondrial function. [Yuan et al., Nature, 2020.]
However, it must be asked whether BAZ-2 and SET-6 would rather mediate age-related physiological adaptation, rather than the agents of aging itself. Indeed their action could reflect a mechanism of adaptation to a progressively more hostile biological environment.
